In the pursuit of optimal gut health, terms like probiotics, prebiotics, synbiotics, and postbiotics are frequently used in Dietary Supplement—but what do they really mean? While they sound similar, each plays a distinct role in supporting digestive and immune health. Below, we break down their differences and benefits to help you make informed choices.
Definition: Probiotics are live microorganisms that, when consumed in adequate amounts, confer health benefits by balancing gut microbiota. They must remain viable to be effective.
Key Strains:
Lactobacillus (e.g., L. acidophilus)
Bifidobacterium (e.g., B. longum)
Saccharomyces boulardii (a beneficial yeast)
Food Sources:
Fermented dairy (yogurt, kefir)
Fermented vegetables (sauerkraut, kimchi)
Fermented soy (natto, tempeh)
Health Benefits:
✔ Restores gut flora balance after antibiotic use
✔ Enhances digestion and nutrient absorption
✔ Boosts immune function by modulating gut-associated lymphoid tissue (GALT)

Definition: Prebiotics refer to non-digestible compounds that selectively stimulate the growth and/or activity of beneficial gut microorganisms (primarily probiotics). Unlike nutrients absorbed by the human body, prebiotics exert their physiological effects exclusively through interactions with probiotics - essentially serving as "microbial fuel" for these beneficial bacteria.
Common Types:
Fructooligosaccharides (FOS)
Galactooligosaccharides (GOS)
Inulin (found in chicory root, garlic, onions)
Food Sources:
Whole grains, bananas, asparagus
Legumes, flaxseeds, Jerusalem artichokes
Health Benefits:
✔ Promotes growth of probiotics (e.g., bifidobacteria)
✔ Improves mineral absorption (calcium, magnesium)
✔ Supports metabolic health by producing short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)
Definition:
Synbiotics are formulations combining probiotics + prebiotics, designed to enhance probiotic survival
and activity in the gut.
Examples:
Bifidobacterium + FOS (supports infant gut health)
Lactobacillus + Inulin (improves lactose digestion)
Advantages Over Probiotics Alone:
✔ Increases probiotic colonization in the gut
✔ Extends probiotic lifespan by providing nourishment
✔ More effective in managing IBS and antibiotic-associated diarrhea

Definition: Postbiotics are non-viable microbial cells or metabolites (e.g., enzymes, peptides, SCFAs) produced during probiotic fermentation.
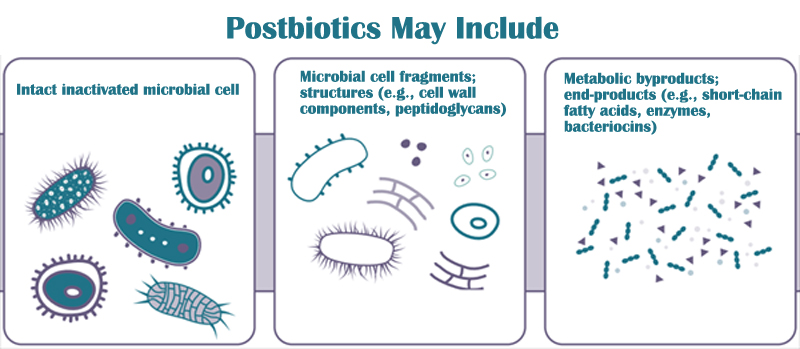
Key Components:
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) (butyrate, acetate)
Bacteriocins (antimicrobial peptides)
Cell wall fragments (immune-modulating effects)
Health Benefits:
✔ More stable than live probiotics (heat/acid-resistant)
✔ Reduces gut inflammation (useful in IBD management)
✔ Enhances immune response by activating regulatory T-cells
However, further clinical trials are needed to validate their efficacy in humans.
Every individual's microbiome is unique—why settle for a one-size-fits-all approach? At Jollywe Supplement, we specialize in personalized probiotic, prebiotic, and postbiotic formulations tailored to your specific health needs.
? Bespoke Synbiotic Blends for targeted gut support
? Clinically Validated Strains for maximum efficacy
? Postbiotic Innovations for enhanced stability and absorption
? Contact us today to design your custom gut health supplement solution!
? +86 13570342869 | ✉ info@jollywe.com
Let us help you build a healthier gut, stronger immunity, and better overall well-being healthy supplement! ?